
Instromet Weather Instruments
Weather stations and weather monitoring specialists
Author: Instromet Weather Systems Ltd
The 0-10V wind sensor! Why use the Instromet 0-10V wind sensor?
The Instromet 0-10V wind sensor is typically used in building automation, industrial control, and HVAC systems for reliable wind speed measurement. Here’s why someone might choose this particular sensor:
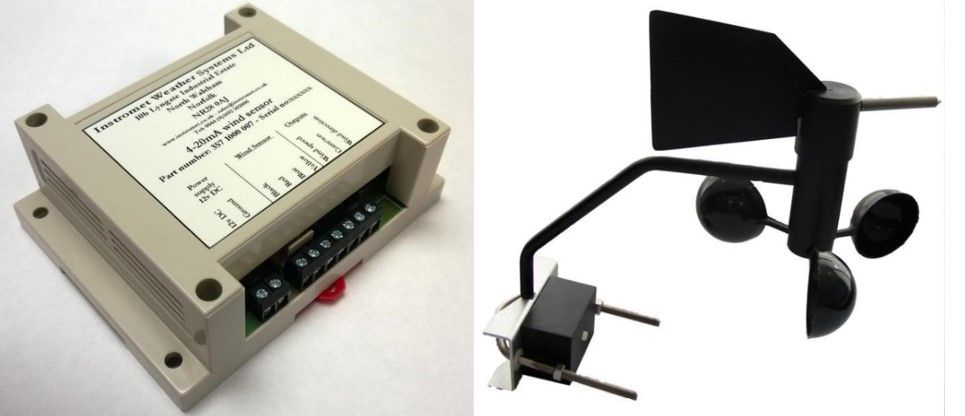
Key Reasons to Use the Instromet 0-10V Wind Sensor
- Analog Output (0-10V)
- This is a standard signal used in many automation systems (e.g., PLCs, BMS).
- Allows easy integration into existing control infrastructure.
- Robust Construction
- Designed for long-term outdoor use, resistant to harsh weather conditions.
- Often used on rooftops, wind-sensitive structures, or industrial sites.
- Reliable Wind Speed Measurement
- Accurate and responsive to changing wind conditions.
- Essential for applications like louver/damper control, awnings, roof venting, or safety systems.
- Simple Installation and Operation
- Supplied with pre-calibrated settings.
- Straightforward wiring for power and signal.
- High quality
- Instromet sensors use sintered bronze or stainless steel ball race bearings giving reducing wear and tear and long operational life.
- Proven Brand
- Instromet is a recognized manufacturer in the weather instrumentation field, especially in the UK and Europe.
- Product Support
- Telephone and email support of all our products available during UK office opening hours for advice, setup help and troubleshooting.
Common Applications:
- Building management systems (BMS)
- Greenhouse automation
- Louver or shutter control
- Weather stations
- Renewable energy systems (e.g., wind turbine control)
- Safety shutdown systems for cranes or tall structures
Buying an Instromet weather station
Buying an Instromet weather station can be a good choice depending on your needs. Here’s a breakdown of the main reasons people choose Instromet over other brands:

Top Reasons to Buy an Instromet Weather Station
1. British Engineering and Manufacturing
Instromet is a UK-based company, and their weather stations are designed and built in Britain. If you’re looking for local craftsmanship, especially in the UK or Europe, this might appeal to you. https://instromet.co.uk/weather-monitoring-systems
2. High Build Quality
These stations are known for their durable materials (e.g., anodised aluminium sensors) and precision engineering. They’re not cheaply mass-produced like some consumer-grade models.
3. Analogue and Digital Options
Instromet offers both classic analogue dial-based systems and more modern digital display units, appealing to users who prefer traditional aesthetics or want more modern data visualization.
4. Customisable and Expandable
Many models allow for add-ons, such as:
- Sunshine sensors
- Extra temperature/humidity sensors
This makes them ideal for enthusiasts or semi-professional use.
5. Accurate and Reliable
Instromet focuses on long-term accuracy, particularly for wind speed, rainfall, barometric pressure, and sunshine duration — key metrics for agriculture, hobbyists, and schools.
6. Good for Educational and Demonstration Purposes
Because of the visible dials and robust build, they’re popular in schools, gardens, and public displays where understanding the weather visually is important.
Things to Consider Before Buying
- Price: Instromet stations are typically more expensive than entry-level consumer brands but reflected in the longevity of the weather stations and sensors.
- Data Connectivity: While some models support computer interfaces, others are less advanced in terms of wireless/app support compared to some rival brands.
- Design Philosophy: They lean more toward mechanical/electro-mechanical elegance than IoT-connected weather tech.
Ideal Buyer Profiles
- Weather enthusiasts who value craftsmanship
- Schools or institutions needing durable display weather stations
- UK/EU customers looking for local support and supply
- People who prefer analogue-style weather data
Buying an Instromet weather station
Instromet Atmos Dual weather station
Atmos Dual weather station introduction
The Atmos Dual weather station was replaced by the Atmos LT in 2012. The Dual had been made since 1995 and was one of the most popular Instromet weather monitors. This weather station feature wind speed (with max gust indicator), wind direction, temperature with min/max, barometric pressure and rain sensing.
Specifications.
- Display unit size: 450 wide x 180mm high x 60mm deep
- Wind direction: Analogue read-out 4 cardinal points sub-divided into 5 degree increments, electronically damped.
- Accuracy: ± 10 degrees, resolution > 10 degrees
- Wind speed: Analogue read-out with gust indicator pointer, calibrated 0- 90 mph, 0-80 knots and Beaufort scale.
- Accuracy: ± 5% or 3 knots
- Barometer: Analogue read-out with set pointer reset, range 950 -1050 mBar (28 -31 inches Hg)
- Temperature: LCD digital read-out in degrees F or C
- Range – 40 to + 50° C (- 40 to + 120° F), resolution 0.1° C
- Rainfall: LCD digital read-out in 0.01mm increments
- Accuracy: ± 5% (5ml of water = 1mm rainfall), resolution 0.01mm auto-sensing
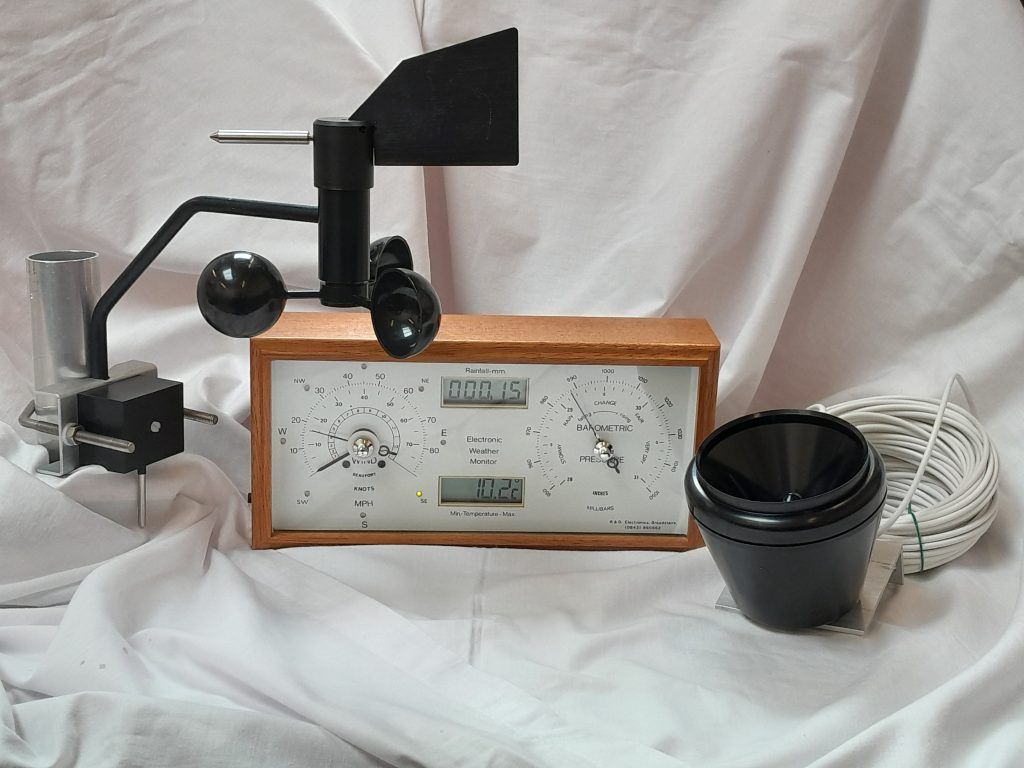
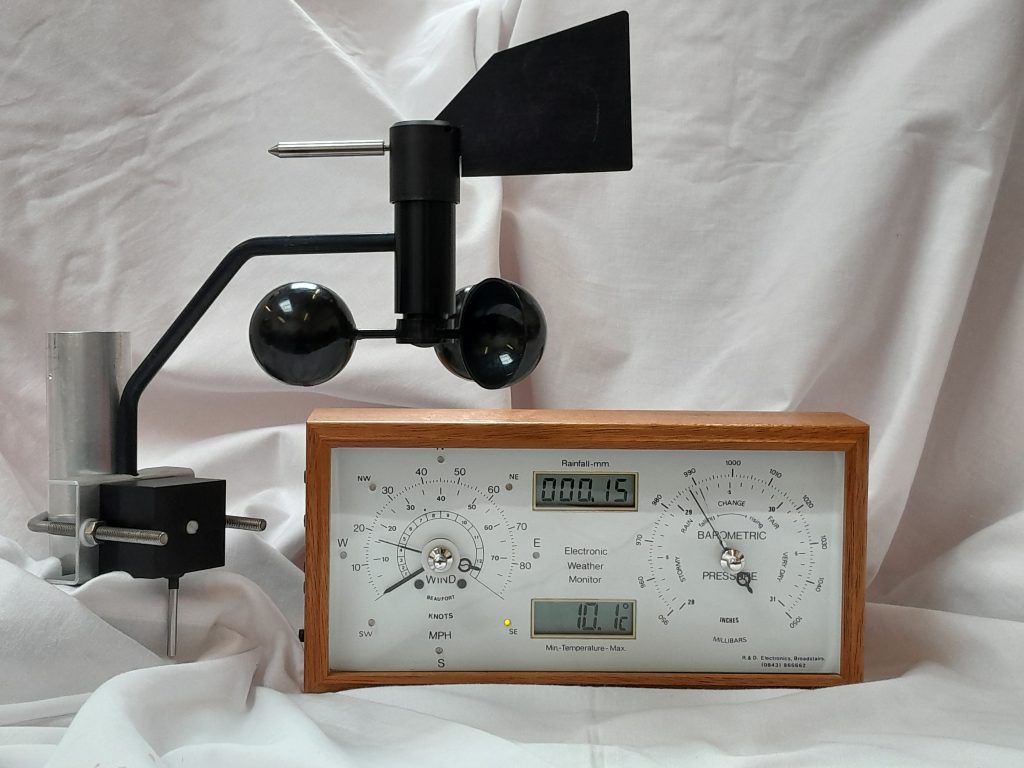
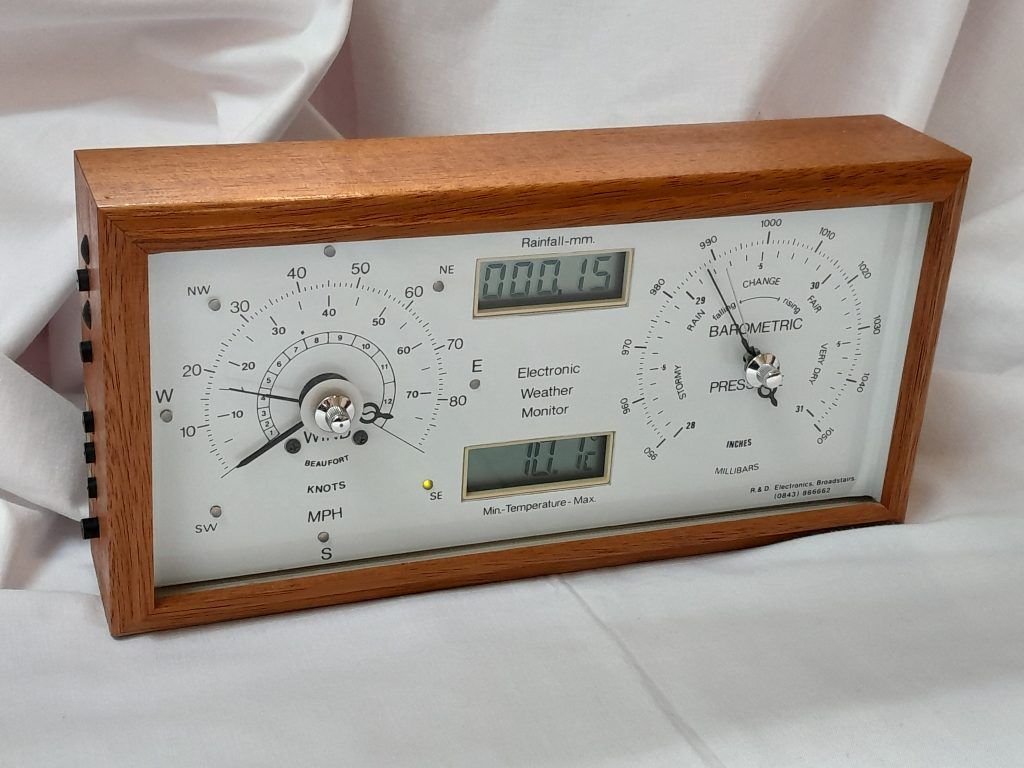




For the latest range of Instromet monitoring products please visit our website at www.instromet.co.uk
Why Do We Measure The Weather?

Why do we measure the weather? Understanding the weather has served great significance over humanity, from planting crops to setting out into the ocean. Predicting how the environment behaves has guided everyday life up to the present.
However, with modern technology, weather measurement and monitoring have grown beyond the need to inform livelihood. It has grown to include efforts to understand how our collective actions have led to where we are now and, more importantly, where we are headed in the future. Here are some of the most compelling reasons why we measure the weather.
1. Why Do We Measure The Weather? People
Most activities depend on the weather conditions, from minor daily decisions to long-term plans. It helps people decide on what they’ll do, the clothes they wear, and even the food they’ll prepare later on.
Weather forecasts have become a staple in regular news programs as it gives you the heads up you need for the upcoming day. Whether you’ll need a raincoat or a hat, or whether it’ll be safe to take the ferry or not, all depends on what are the expected conditions for today. With access to better technology and larger data sets, weather forecasting has become more accurate and more reliable. The latest weather updates are available right from your fingertips, allowing you to observe weather conditions anytime.
This capability also applies to long-term planning. Despite the drastic changes in meteorological patterns due to climate change, forecasts remained relatively accurate. Our ability to predict weather and climate conditions continue to keep up with the changing trends thanks to evolving weather measurement and monitoring instruments.
2. Livelihood
As mentioned, livelihood has always been a critical driver for measuring and predicting the weather. Many industries heavily depend on climate and weather, as they’ve done for hundreds of years.
Humanity learned to settle in one place when they learned how to plant crops for sustenance. Since then, it has become imperative to know when rain falls, or droughts are more likely to occur. These pieces of information are essential in finding the best time to start planting and when to harvest crops. Although humankind has nearly perfected the cycle of the seasons and the planting schedules, rapid changes and unstable conditions threaten the farmers’ ability to plant and harvest.
Aside from planting crops, animal domestication is another field that requires a good understanding of the weather. Like crops, livestock is also an essential part of the human food supply. Being unable to care for animals could upset their store, causing food security issues that can threaten many lives down the line. By having a good grasp of weather conditions, people in these industries can carefully plan when to allow the animals to graze or stock up on the animal feed.
3. Transport
Before, weather prediction told humans when it was safe to set off on boats and go fishing. The same idea continues today but on a much larger scale—weather measurement and monitoring impact a vast global industry, from small fisherfolk to large shipping vessels.
Industrial fishing vessels, cargo freighters, and even oil tankers depend on modern technology to safely and efficiently ply their trades. It is essential to know if there’s a storm brewing down their path days or weeks in advance to avoid unnecessary risks. Modern marine vessels now use weather routing technology, which uses the latest weather information available to guide shipping routes and travel plans. Networks of sensors and monitoring systems provide insights on wind and currents, guiding navigators and sailors of weather conditions ahead of them.
The importance of weather prediction is not limited to marine transport too. Airlines also need timely and accurate information on the environment. Pilots, like sailors, need to know what lies ahead. Irregular or unstable air currents cause turbulence, while potential rains also affect visibility in the sky.
4. Science
By measuring the weather, we learn more about it, which allows us to develop better and more accurate systems. Before, people recorded how the phases of the moon or fluctuations in airflow give hints on upcoming tides and storms. We have sensors installed on ocean buoys or weather balloons–scattered around the world to collect information without the need for an actual person to go and manually monitor those places.
Furthermore, technology has enabled people to gather more data and process them more efficiently. Artificial intelligence and machine learning are becoming increasingly important because of their ability to handle large amounts of data. With these tools, people can now make projections about meteorological conditions far into the future.
The same technologies are being used to assess how our actions impact the environment. Visualizations of past and present carbon emissions now help explain how climate change continues to evolve and how it threatens our future. In doing so, experts can recommend what collective actions are available to mitigate or even reverse this phenomenon.
Final Word
Measuring the weather is a vital endeavor. It affects our immediate plans and activities and our entire future as a species. As we better understand how the world works, we’ve also found ways to use it for our development. Thanks to predicting weather far into the future, we’ve had entire fleets of aircraft and networks of ships traveling in perfect unison.
More importantly, technology has allowed us to finally see how we impact the environment and how it affects us in return. We can identify options on how we can reverse the damage done and secure the world for future generations.
Article Contributor: Bash Sarmiento
Weather Observation Equipment and The Social Influences It Has Made

Weather Observation
Weather observation; It was not until the advent of the weather instrument that meteorology became a science. Meteorology was a key topic of discussion among the Greek philosophers, and many of those later involved in weather forecasting used their ideas.
Now, weather instrumentation allows us to predict and measure to the hour and in real-time. To appreciate this, we need to understand the history of weather observation equipment and how society influenced its development.
Instrumentation In Ancient History
Early civilizations monitored seasonal changes in the weather using recurrent astronomical and meteorological events. Babylonians attempted to predict short-term weather changes around 650 B.C based on optical phenomena such as haloes and clouds.
In 300 B.C., Chinese astronomers created a calendar where each holiday was associated with a particular kind of weather.
For centuries, forecasts have been produced based on weather lore and personal observation. By the end of the Renaissance, scientists realized the speculations of natural philosophers had become insufficient.
Further knowledge was needed to understand the atmosphere better. The atmospheric properties were measured using instruments, such as moisture, temperature, and pressure.
Invention of Weather Instrumentation
In the mid-fifteenth century, Nicholas Cusa described the first hygrometer design in western civilization. The first standard rain gauge was invented in 1441 by king Sejong’s son, Prince Munjong. In Korea, these were used to assess land taxes based on a farmer’s potential harvest during the Joseon Dynasty.
In the mid-17th century, Evangelista Torricelli invented the mercury barometer by an Italian mathematician and physicist. There was also the development of a reliable thermometer simultaneously, founding the basis for modern weather measurement. While gas thermometers were available even during Galileo’s time, they were unreasonable and defective.
With a mercury-type thermometer, Gabriel Fahrenheit developed a reliable scale for measuring temperature in 1714. In 1742, a Swedish astronomer named Anders Celsius proposed the ‘centigrade’ temperature scale.
Horacio Benedict de Saussure was the first to demonstrate a hair hygrometer in 1783. A system of grading wind speeds was introduced in 1806, devised by Francis Beaufort.
Marine weather sensor technology has advanced rapidly over the past half a century. These can provide visual images and data that can be used to calculate temperature and humidity profiles and other environmental variables.
Modern Weather Observation Equipment
With the development of weather instrumentation came the introduction of satellites in 1958. Today, these satellites give us global coverage and high-time resolution data. This data is used to develop accurate weather forecasts, which are also used in disaster management.
The advent of weather observation equipment led to significant improvements in society, especially concerning agriculture. With accurate predictions and measurements, farmers could plan their planting and harvesting strategies more effectively.
With photocells and other technologies, weather stations are used for many different applications. Weather stations allow meteorologists to observe critical data, such as temperature, humidity, rainfall, wind speed, wind direction, barometric pressure, and current barometric pressure trends.
Recently, radar network sensors have been developed. These can detect and report the movement of precipitation. The advent of better weather observation equipment has led to better weather forecasts, which has enabled more individuals to plan their daily activities accordingly.
Weather instruments such as weather balloons, remote sensors, and ground-based weather stations provide us with weather information. These sensors provide temperature, pressure, humidity, wind, rain, snow, solar radiation, and clouds. Weather sensors are also used to develop short-term weather forecasts, which meteorologists then use to develop longer-term forecasts.
Social Impact of Weather Observation Equipment
Meteorology plays a crucial role in society today. From predicting the weather, forecasting disasters, and providing weather warnings, weather forecasting has come a long way. It contributes to planning, transportation, agriculture, and industry.
With the advancement of weather instrumentation came the improvement in weather forecasting. The improved weather forecasts led to more precision in activities like agriculture, which led to an increase in crop yields.
Weather stations are also used to measure air pollution and to predict hurricane movement. These technologies also led to satellite networks and radar networks, which provide information about atmospheric conditions to meteorologists.
The advent of weather instrumentation led to more precision in activities like agriculture, which led to an increase in crop yields. It also led to satellite networks and radar networks, which provide information about atmospheric conditions to meteorologists.
Farmers tend to plant and harvest their crops based on seasonal weather predictions. Otherwise, they will plant when there is insufficient rainfall and harvest when the rains start. This can result in crops being ruined. They also use weather forecasts to determine when to apply fertilizer. By understanding the amount of rainfall, farmers know when to fertilize their crops.
Weather observation equipment is also critical in aviation. Air traffic controllers use reports produced by weather equipment to make crucial decisions. They also use this information to plan operations.
Weather observation equipment is also used in the transportation industry, whether it’s for land, sea, or air transport. Airlines, for example, use weather observation equipment to determine flight levels. This allows them to plan routes based on factors such as wind.
Future of Weather Equipment
The field of meteorology is constantly evolving. New technologies are being developed, leading to better weather forecasts. New weather mapping systems are being designed to contribute to accurate weather forecasts.
The advent of new weather observation equipment will lead to more accurate weather forecasts. This will lead to better planning, which will benefit agriculture, aviation, and the transportation industry.
With climate change and global warming, extreme weather has become the norm. We rely heavily on weather equipment to detect and report climate changes. Weather stations use sensors to detect climate change, which is used to improve forecasts.
New technology is being developed. These include sensors, software, and networks. These are being developed to improve the accuracy of weather forecasts. They also allow for better monitoring of the environment.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning provide significant benefits for weather forecasters. With AI, forecasters can process more data more rapidly, which helps them develop more accurate forecasts. With machine learning, forecasters can obtain more data about past weather, which helps them identify patterns and predict future weather.
Predicting weather better and more efficiently will improve our day-to-day lives. Weather equipment will continue to be developed to enhance our ability to make better weather predictions.
Final Thoughts
The importance of weather instrumentation is that it provides real-time data, allowing meteorologists to develop accurate weather forecasts. This data is also useful to farmers, the aviation industry, and the transportation industry.
Weather instrumentation will continue to play an essential role in our lives. New technology is being developed, leading to better weather forecasts. Appreciating the history of weather equipment yesterday can help you build on a better future tomorrow.
Article Contributor: Bash Sarmiento
How Weather Watching Originated
Weather Watching history with Instromet by Bash Sarmiento

Weather watching is an essential scientific practice. It lets us prepare ourselves for what nature decides to bring us on that day. It’s often taken for granted that for the longest time, humans had no way of telling what the weather was going to be like past hunches. The history of weather watching is fascinating and it would be a disservice to not talk about it. So, that’s exactly what we’re going to be doing today.
What is Weather Watching?
Weather watching is the in-depth observation of weather patterns using quality-controlled prediction models. Weather watching can be done on either a local or global scale. Without the comprehensive weather reports provided by weather watchers, people would not be able to prepare themselves for sudden weather changes.
Weather watching is done through observations of pressure, moisture, wind speed, wind direction, and temperature. The consistency of all these factors since the earliest weather observations has helped in making predictions much easier. In addition to that, the advancements in weather forecasting technology have made weather updates more accurate than ever before.
History of the Radcliffe Observatory
The Radcliffe Observatory is one of the earliest, if not the earliest, weather observatories ever recorded. It has records from as far back as 1772, which gives us insight into what the weather was like hundreds of years ago. The Radcliffe Observatory boasts the longest single-site weather records in the UK and one of the longest in the entire world.
Its creation was thanks to one Dr. Thomas Hornsby (1733-1810), a Savilian Professor of Astronomy. He was entrusted with the funds for the construction of a large observatory as well as all the proper equipment. The building began in 1772 by the Radcliffe Trustees, who promptly gave Hornsby the title of Radcliffe Observer.
The research they took started with observations of air temperature, but surprisingly enough, for astronomical refraction, not the weather. Slowly but surely though, Hornsby began observing the weather until the date of his death in 1810. All of these records are recorded in the annual volumes of the Radcliffe Astronomical, which began in 1849.
For equipment, they would often use very rudimentary thermometers. However, the observatory was always kept up to date with the latest in forecasting technology. In fact, many of the innovations for weather forecasting in the UK stemmed from Radcliffe. Famous institutions include Kew, Greenwich, and Oxford.
The 1850s was when the records started becoming more in-depth and frequent. Photographic and autographic instruments were used to provide more consistent records of rainfall, wind, and temperature. 1881 to the present is complete and reliable, as dictated by the Met Office.
Radcliffe Observatory’s constant observations since its inception to the present day have been a major benefit to weather watching. The link it provides between the weather from hundreds of years ago and the weather today is essential to understanding our world.
History of Weston Park Weather Station
Another important weather station in the UK showcases the importance of weather watching to the general public outside of scientific advancements. The creation of Weston Park Weather Station is because of an outbreak of bacterial infections in Sheffield back in 1882.
In fact, this particular use for weather watching is still applied to this day with the recent COVID-19 epidemic. By analyzing the temperature and humidity in the different areas infected with COVID-19 (or not), scientists should be able to determine when an outbreak may next occur and act accordingly.
Elijah Howarth, dubbed “The Prophet”, believed that understanding weather conditions, especially temperature, would help let the local doctors know if an outbreak was going to be likely. The station’s first equipment was bought with the help of a small department in the Board of Trade.
That small department would soon become the Met Office, the main meteorological authority in the UK. Weston Park is one of the Met Office’s first official weather stations for this reason. Its longevity, along with Radcliffe, is why it’s considered one of the most important weather stations in the entire country.
To this day, Weston Park continues to record weather patterns using various techniques and equipment such as state-of-the-art thermometers, barometers, and weather drifting buoys.
Weather Watching – Conclusion
The history of weather watching is an important period in scientific history. There’s a lot of benefits to be learned from how observations were recorded back then as opposed to how the weather is recorded now. Determining what the climate is going to be like in the future is important not just for scientific study, but for socio-economic reasons.
After all, the weather affects more than just forecasting equipment. Important activities such as farming, disaster prevention, and travel are all reliant on accurate weather predictions. To constantly improve our current weather forecasting technology, it’s important to look back on how our predecessors did things with much less equipment.
Article Contributor: Bash Sarmiento
Weather today – The Instromet Climatica Basic
What ever way the wind blows; Looking good with an Instromet system

The weather today has never been more interesting. The Climatica Basic was one of the original R&D Electronic weather stations. Due to changes in technology and availability of parts it was discontinued. The Climatica Basic hasn’t been made by Instromet since 2012.
The Climatica basic displays wind speed in miles per hour, Knots and Beaufort. It has a gust pointer to show the highest gale. The wind direction is also shown on a dial indicator with compass point graduations.
Weather station features
The Climatica Basic would have been supplied as a complete system with display, junction box, wind sensor and 25 metre sensor cable. These displays are compatible with the current wind sensors we make and supply.
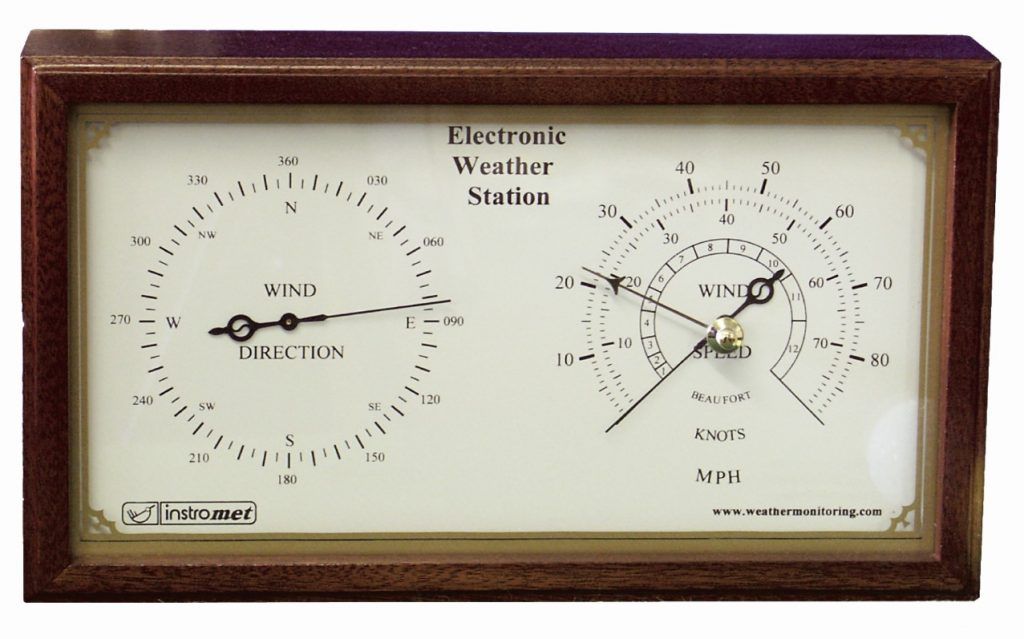

For the latest range of Instromet monitoring products please visit our website at www.instromet.co.uk
Industrial wind sensor 0-10V & 4-20mA product description

There are a number of different applications for the Instromet industrial wind sensor. They are typically connected to a PLC to enable control of ancillary electrical equipment in higher wind conditions. Please see more details of ‘where used’ and ‘typical applications’ below. There are multiple other applications for these wind sensors and please contact us for more details and to let us know where you use your wind sensor.
0-10V wind speed & direction sensor – part no. 357 1000 005
0-10V wind speed & direction sensor DIN rail case – part no. 357 1000 010
4-20mA wind speed & direction sensor – part no. 357 1000 001
4-20mA wind speed & direction sensor DIN rail case – part no. 357 1000 008
Wind sensor – where used
- Building Maintenance Systems.
- As part of a weather monitoring system.
- Wind turbine site testing & control applications.
- Ventilation and air extraction systems.
- With structures and equipment vulnerable to high winds (aerials, awnings, etc).
- Windows, vents and skylights.
- With inflatable structures (such as tennis courts).
- Plaza fountains.
- Roller shutter doors and electric gates.
- Numerous other processing plant, factory, industrial and commercial sites.
Typical applications.
(Note the Instromet wind switch can also be used for many of these applications where a PLC is not available).
- Building Maintenance Systems (BMS) to switch on fans, open vents and control equipment.
- Measuring and recording wind speeds & directions for real-time monitoring, historical recording & site assessment.
- Suitability site testing for wind turbines.
- Ventilation and air extraction systems – switching fans on/off, switching opening & closing vents, etc.
- Signalling lowering mechanism on aerials and opening & closing awnings.
- Closing roller shutter doors, gates, windows and skylights in higher winds.
- Operating fans on inflatable structures (such as tennis courts) to make them safe in high winds.
- Operating reducing pump pressure on plaza fountains in high winds.
- Numerous other safety applications, control and operational applications.